Alkene alkyl halide alcohol phenol amine aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid. The alcohol is the product of an S N 1 reaction and the alkene is the product of the E1 reaction.
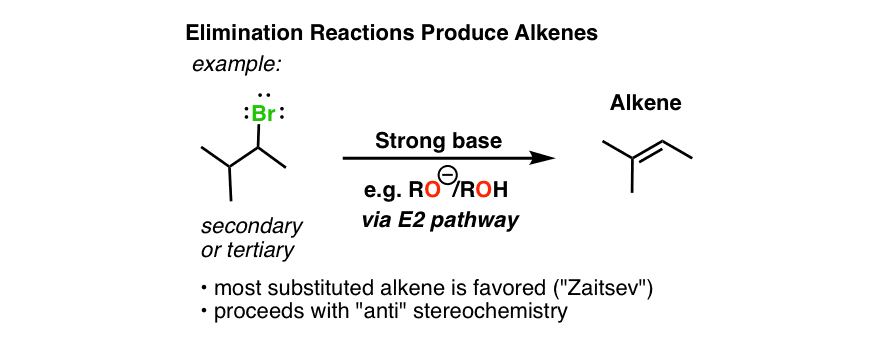
Alkyl Halide Reaction Map 14 Key Reactions Of Alkyl Halides

4 5 Bonding In Alcohols And Alkyl Halides
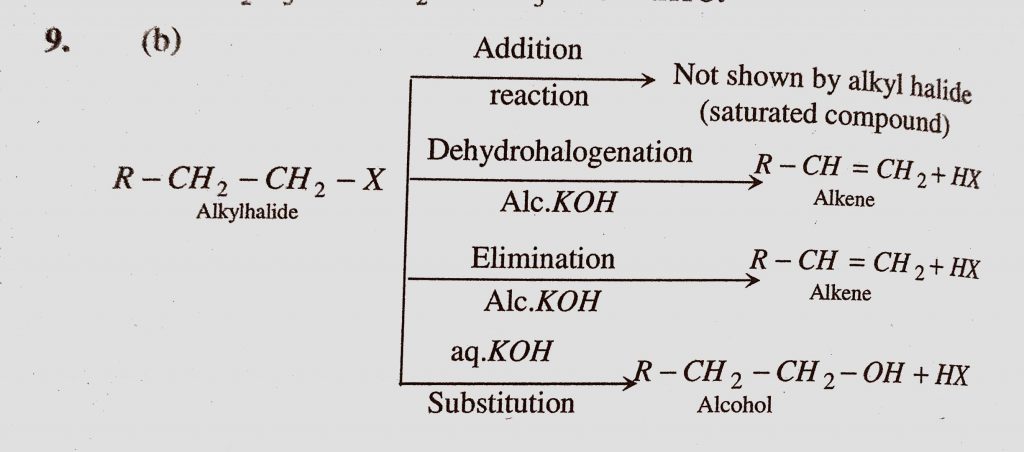
An Alkyl Halide May Be Converted Into An Alcohol By A Addition B Substitution C Dehydrohalogenation D Elimination Sahay Lms
It reacts with numerous inorganic compounds including water carbon dioxide and oxygen and with most kinds of organic compounds.

Alkyl halide to alcohol. The Lucas reagent is a solution of ZnCl2 in concentrated HCl. The alkyl group is a type of functional group that has a carbon and hydrogen atom present in its structure. Halide reactivity increases in the order.
An acid halide can be converted to an ester by an acid catalyzed reaction with an alcohol. 60 and 2-methylpropene 40 at a rate independent of the water concentration. Compound B is reacted with H B r to give C which is an isomer of A.
From Grignard on 6. Reacting a primary amine with an acid halide creates an Nsubstituted amide. More about Grignard Reagent.
2-Phosphotransferases with a carboxy group as acceptor. Alkyl halides can also be formed by reaction of alcohols with H-X acids. An anhydride may be produced by reacting an acid halide with the sodium salt of a carboxylic acid.
Primary alkyl halide A C 4 H 9 B r reacted with alcoholic K O H to give compound B. When more than one alkene product is possible from the base induced elimination of an alkyl halide the most highly substituted most stable alkene is usually the major product. RX HR _ Helimination H RH R 2 alkyl halide Elimination is a competitive reaction with nucleophilic substitution.
The Grignard reagent has the general formula R MgX and the general name alkyl magnesium halide. Inversion results because the pyridine reacts with ROSOCl to give ROSONC 5 H 5 before anything further can take place. Contain only a single type of these functional groups.
Rearrangements stereochemistry racemization C H. In the past ten years metal halide perovskites have attracted great interest from the scientific community leading to numerous studies elucidating the physical properties of the material and developing a large variety of optoelectronic devices solar cells photodetectors including x-ray detectors light emitting diodes lasers. C bonded to SH group C SH Sulfide.
The addition of pyridine to the mixture of alcohol and thionyl chloride results in the formation of alkyl halide with inverted configuration. C bonded O of a hydroxyl group C OH Ether. In these latter two cases there is only one organic group R so that the terms are used to designate the type of carbon to which the alcohol or halide function is attached.
Your final task for today is to determine whether the Lucas reagent promotes SN1 or SN2 reactions by examining how the reaction rate varies with the structure of the alcohol. 3-Phosphotransferases with a nitrogenous group as. 1 alkyl halide SN2 RCCCH2R RCC.
Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula RX where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen F Cl Br I. C bonded to N C N Thiol. The OH is a poor leaving group but OH 2 is an excellent leaving group and once the -OH is protonated the.
Conversion of an alcohol to an alkyl halide R-OH R-X Chapter 107 1Substitution reaction of alcohols with HX R-OH HX R-X H 2O Works better with more substituted alcohols S N1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate. The general formula for an alkyl group is CnH2n1 where n represents a number or integer. Alkyl or Aryl Acids Alkyl group can be 1º 2º or 3º Mechanism required.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bondd l ided to an Electronegative Atom Alkyl halideAlkyl halide. Lucas test for alcohol ROH reactivity. The equilibrium position of the reaction depends on the nucleophilicity of the anion whether a good leaving group is present and whether one anion is better stabilized than the other in a given solvent see Nucleophilic SubstitutionFor example reactions with KF will thus lead cleanly to fluoroalkanes because fluoride is such a poor leaving group due.
The Grignard reagent is highly reactive. In organic chemistry an alkane or paraffin a historical trivial name that also has other meanings is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbonIn other words an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carboncarbon bonds are single. This group forms by reacting the salt of a carboxylic acid with an acyl halide.
When A was reacted with N a metal it gave a compound C 8 H 1 8 that was different than the compound when n. Alkyl halide alcohol ether sulfonium ion X F Cl Br I RO R amine RN H 2 RS R R N R R R R quaternary ammonium ion pKa of conjugate acid of the leaving group 10 to 32 15 15 40 10 sulfonate ester RO S O O R 6 6 101 NucLeophiLic SuBStitutioN ReactioNS of aLcohoLS. Haloalkanes have been known for centuries.
Alkyl Halide Carbon-heteroatom single bonds CO COC alcohol sethr H CN amines CS H CS thiols sulfides disulfides acidic basic HO opsin Lys-NH2 HN H Lys- opsin rhodpsin Carbon-nitrogen multiple bonds N imine Schiff base CCN nitrile cyano group basic CH O CC O Carbonyl-oxygen double bonds carbonyls aldehyde ketones CO O H CO O C. Hydrolysis Section 20-8C R OH O RCN H H 2O Mechanism not required. Two Cs bonded to same S C S C.
C bonded to halogen CC bonded to halogen C-X Alcohol. Two Cs bonded to the same O C O C Amine. 2-In P-halide compounds.
R-OH H-Br R-Br H 2 O In acidic media the alcohol is in equilibrium with its protonated form. Chloroethane was produced in the 15th century. The characteristics of these two reaction mechanisms are similar as expected.
Mechanism of the Finkelstein Reaction. The halogen is converted to halide anion and the carbon bonds to the metal the carbon has carbanionic character. Evidence for this mechanism is as follows.
1-Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor. The Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide Grignard reagent to a ketone or aldehyde to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol respectively. Each compound will.
The following equations illustrate these reactions for the commonly used metals lithium and magnesium R may be hydrogen or alkyl groups in any combination. Alkanes have the general chemical formula C n H 2n2The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of. Loss of an alkyl radical by α-cleavage occurs mostly in methyl esters mz 59 McLafferty rearrangements are possible on both alkyl and alkoxy sides Benzyloxy esters and o-alkyl benzoates fragment to lose ketene and alcohol respectively Amides M usually observed.
The reaction with formaldehyde leads to. The designation of amines as primary secondary and tertiary is different from the usage of these terms in connection with alcohols and alkyl halides. H R O O R OH O-Protonate Access.
Each of these functional groups has a unique combination of solubility and reactivity that allows it to be distinguished from the others. Acting on halide bonds. Alkyl or Aryl Halide Mg ether MgX Grignard Reagent 1.
Following is the anhydride group. Note that the base attacks the alkyl halide from the side opposite the halogen. Follow the Nitrogen Rule odd of N odd MW.
Carboxylic acids react with phosphorous trichloride PCl 3 phosphorous pentachloride PCl 5 thionyl chloride SOC l 2 and phosphorous tribromide PBr 3 to form acyl halides. Reacting ammonia with an acid halide produces an amide. Transferring alkyl or aryl groups other than methyl groups.
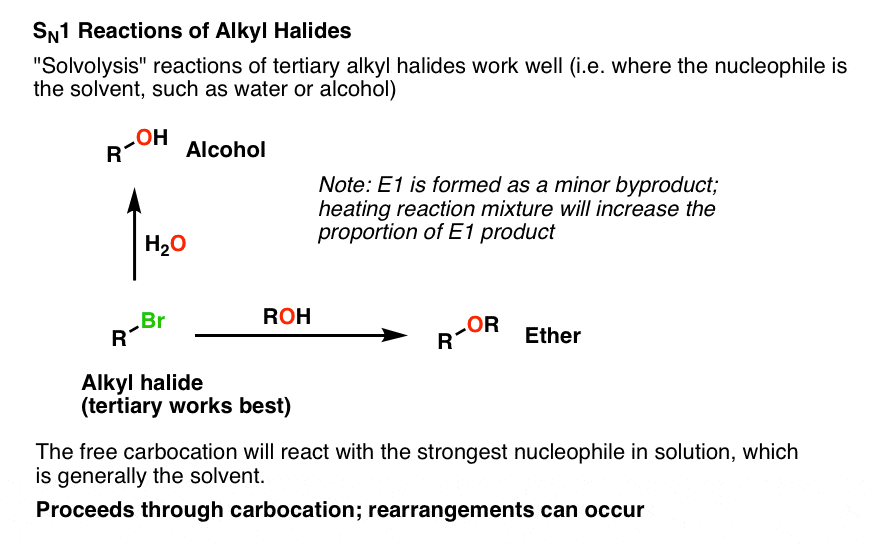
Alkyl Halide Reaction Map 14 Key Reactions Of Alkyl Halides
How Can We Convert Alkane To Alcohol Quora

Ch 8 Rx Substitutions

Chapter 4 Alcohols And Alkyl Halides Functional Groups

Alcohol Reactions Of Alcohols Britannica

Sn1 Reaction Of Ethanol At Tertiary Alkyl Halide Chemistry Stack Exchange

Alcohol Reaction With Hcl Hbr And Hi Acids Chemistry Steps
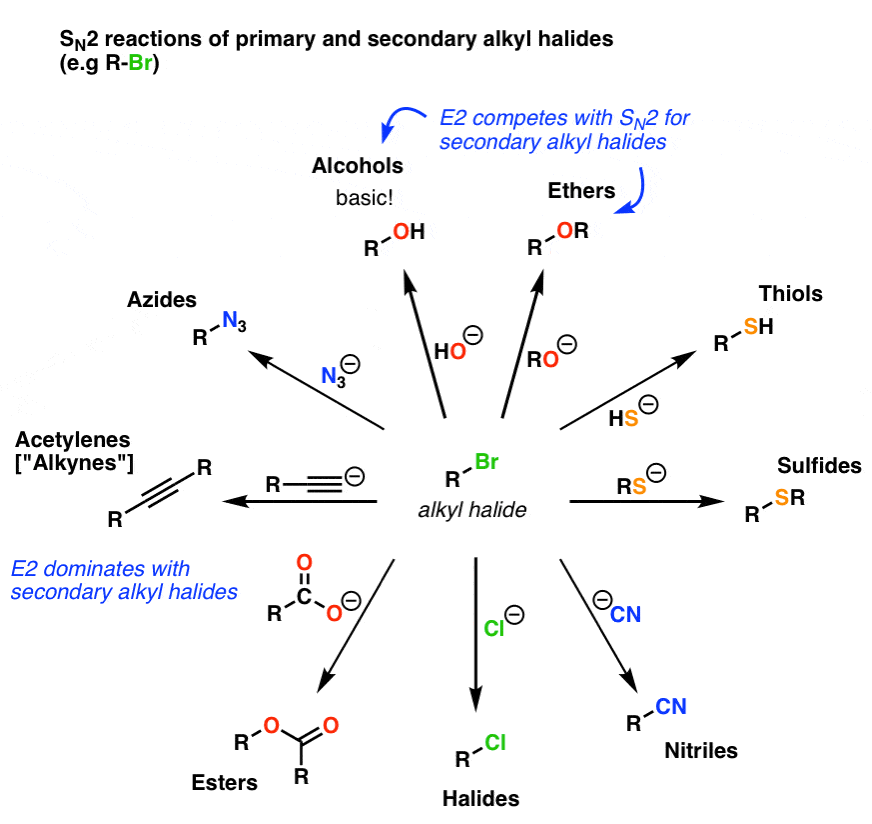
Alkyl Halide Reaction Map 14 Key Reactions Of Alkyl Halides

